what mass (in g) of mnso4 h2) is needed to prepare a 50.0ml of 350ppm mnso4
Table of Contents
AimTheoryMaterials RequiredApparatus SetupProcedureObservationCalculationsResults and DiscussionPrecautionsViva Questions
The titration of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) against oxalic acrid (CiiH2O4) is an case of redox titration. In close proximity to the endpoint, the activity of the indicator is coordinating to the other types of visual colour titrations in oxidation-reduction (redox) titrations.
Aim:
To determine the force of potassium permanganate past titrating it against the standard solution of 0.1M oxalic acid.
Theory:
Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidising agent and in the presence of sulfuric acid it acts equally a powerful oxidising agent. In acidic medium the oxidising ability of KMnOfour is represented by the following equation.
In acidic solution,
MnO4 – + 8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O
Solution containing MnO4 – ions are purple in colour and the solution containing Mntwo+ ions are colourless and hence permanganate solution is decolourised when added to a solution of a reducing agent. The moment there is an excess of potassium permanganate present the solution becomes purple. Thus, KMnO4 serves as self indicator in acidic solution.
Potassium permanganate is standardized confronting pure oxalic acid. Information technology involves a redox reaction. Oxalic acrid is oxidised to carbon dioxide by KMnO4, which itself gets reduced to MnSO4. Oxalic acid reacts with potassium permanganate in the following way.
The chemic reaction at room temperature is given below.
Reduction Half reaction:- 2KMnO4 + 3H2And so4 → Chiliad2SOiv + 2MnSOiv + 3H2O + 5[O]
Oxidation Half reaction:- 5(COOH)ii + 5[O] → 5H2O + 10COtwo↑
The overall reaction takes place in the process is
Overall reaction:- 2KMnOfour + 3HtwoSOfour + five(COOH)two → KiiAnd soiv + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 10CO2↑
The ionic equation involved in the process is given below.
Reduction Half reaction:- [MnO4 – + 8H+ + 5e– → Mnii+ + 4HiiO] ten 2
Oxidation Half reaction:- [C2O4 2- → 2CO2 + 2e–] ten 5
Overall Ionic reaction:- 2MnO4 – + 16H+ + 5CtwoO4 2- → 2Mnii+ + 10CO2 + 8H2O
This titration cannot exist carried out in the presence of acids similar nitric acid or hydrochloric acid considering itself is an oxidising agent. And then hydrochloric acid chemically reacts with KMnOiv solution forming chlorine which is also an oxidising amanuensis.
Materials Required:
- Oxalic acid
- Potassium permanganate solution
- one.0M sulfuric acid
- Chemic residual
- Burette
- Burette stand
- Pipette
- Conical flask
- Funnel
- Measuring flask
- Weighing bottle
- White tile
- Burnet
- Wire gauze
Apparatus Setup:
- In burette – KMnOfour solution
- In Conical flask – 10ml of oxalic acid + Sulfuric acid
- Indicator – Self indicator (KMnO4)
- End Point – Advent of permanent stake pink color.
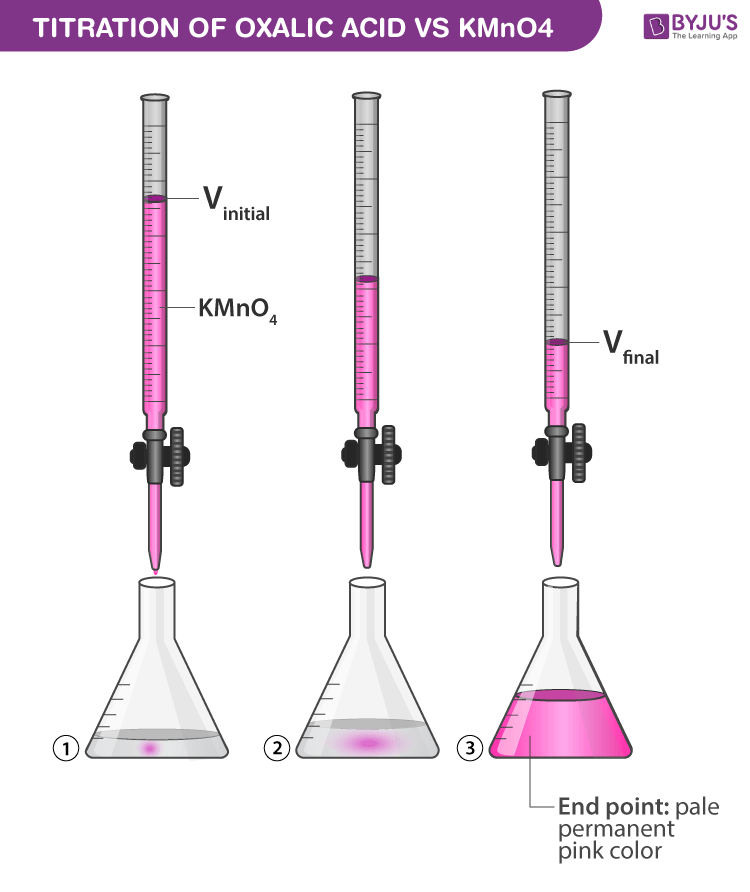
Titration of Oxalic Acrid with KMnO4
Process:
(a) Preparation of 0.1N standard solution of oxalic acid:
The quantity of oxalic acid required for the 250ml of the solution having a normality of 0.1N can be calculated equally follows.
Equivalent weight of oxalic acrid = Molecular weight/No of electrons lost by one molecule
Equivalent weight of oxalic acid = 126/2 = 63
Strength = Normality ten Equivalent weight
Forcefulness = one/x 10 63 = six.3 m/l
For the grooming of i litre of N/ten oxalic acid solution amount of oxalic acrid required = half dozen.3 g
- Weigh an empty lookout drinking glass using a chemical balance.
- Weigh 6.3g of oxalic acrid accurately in the lookout glass.
- With the aid of a funnel transfer the oxalic acid into the measuring flask.
- Now wash the funnel with distilled h2o without removing the funnel from the flask.
- Make the solution upwardly to the marked bespeak with distilled water and brand sure the oxalic acid is fully dissolved.
- This solution is 0.1N standard solution of oxalic acid.
(b) Titration of potassium permanganate solution against standard oxalic acid solution:
- Rinse the burette with the potassium permanganate solution and fill the burette with potassium permanganate solution.
- Fix the burette in the burette stand up and place the white tile beneath the burette in order to find the end bespeak correctly.
- Pipette out 10ml of 0.1N standard oxalic acid solution in a conical flask.
- Add a test tube full of sulfuric acid in gild to foreclose oxidation of manganese to course manganese dioxide.
- Heat the mixture upto sixtyoC before titrating with potassium permanganate.
- Notation downward the initial reading in the burette earlier starting the titration.
- The hot solution is titrated against potassium permanganate solution and simultaneously swirl the solution in the flask gently.
- Initially the regal colour of KMnO4 is discharged with oxalic acid. The appearance of permanent pink colour reveals the stop betoken.
- Repeat the titration until concordant values are obtained.
- Note downwards the upper meniscus on the burette readings. Record the reading in the observation table given beneath in order to calculate the molarity of KMnO4 given.
Ascertainment:
| S.No | Volume of oxalic acid in ml | Burette Reading | Volume(V) of KMnOiv used 5 = (y-x)ml | |
| Initial(10) | Final(y) | |||
Calculations:
To calculate the strength of given KMnO4 in terms of molarity the following formula is used
a1GrandoneFive1 = a2MiiV2
Where a1 and a2 are stoichiometric coefficient of oxalic acrid and KMnO4 in a counterbalanced chemical equation.
aone = 2
a2 = 5
Where
1000ii and Thousandi are molarities of potassium permanganate and oxalic acrid solutions used in the titration.
5two and V1 are the book of potassium permanganate and oxalic acid solutions used in the titration.
Therefore,
KMnOiv = Oxalic acid
5MiiV2 = 2M1Vane
Chiliadii = (2M1V1/5MiiVtwo)
The forcefulness of KMnO4 is calculated past using the molarity.
Forcefulness = Molarity ten Molar mass
Results and Give-and-take:
- Molarity of KMnO4 is ______
- The Strength of KMnO4 is _____M.
Precautions:
- Clean all the apparatus with distilled water before starting the experiment and then ascension with the solution to be taken in them.
- Rinse the pipette and burette before use.
- Potassium permanganate is night in color, and so e'er read the upper meniscus.
- Use dilute sulfuric acrid for acidifying the potassium permanganate.
- Take authentic readings one time it reaches the terminate point and don't get with average readings.
- Use antiparallex carte du jour or autoparallex menu while taking the burette readings.
- Practise not apply condom cork burette every bit it is tin can be attacked by KMnO4.
- The forcefulness of the unknown solution should exist taken upto 2 decimal places just.
Viva Questions
How to convert Thou/10 oxalic acid solution into Northward/10 oxalic acid solution?
To make the conversion add an equal book of h2o and then that the solution converted to N/10.
What is the formula and basicity of oxalic acrid?
The formula for oxalic acid is (COOH)two.2H2O. The basicity of oxalic acrid is 2 means information technology is a dibasic acid.
In this titration of KMnO4 vs oxalic acid, what is the indicator used?
Potassium permanganate itself is regal in colour and acts equally a cocky indicator.
What is meant by endpoint?
The endpoint, which is also called equivalence point or stoichiometric point means the conclusion of the chemical reaction. Information technology is the point where no more than titrant is required and the reaction is consummate.
What is meant by redox titration?
In redox titrations, both oxidation and reduction reactions take place simultaneously. During titration, one will get oxidised at the same time the other reactant volition go reduced as well called a redox reaction.
Recommended Videos

Likewise Cheque more on:
- Chemistry Important Questions for Form 12 & 11
- Class 12 Chemistry MCQs
- Form 11 Chemistry MCQs
- Class 10 Chemical science MCQs
- Class 9 Chemistry MCQs
Go along visiting BYJU'S to learn more about Grade 12 CBSE chemical science practicals.
mcclainthioseen37.blogspot.com
Source: https://byjus.com/chemistry/titration-of-oxalic-acid-with-kmno4/
0 Response to "what mass (in g) of mnso4 h2) is needed to prepare a 50.0ml of 350ppm mnso4"
Post a Comment